Understanding On-Grid Solar Systems: Powering the Future with the Sun
In the modern era of sustainable living and renewable energy, solar power has emerged as a reliable and eco-friendly solution to our growing energy needs. Among the various types of solar installations, the on-grid solar system—also known as a grid-tied solar system—is one of the most popular and widely used configurations, especially in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
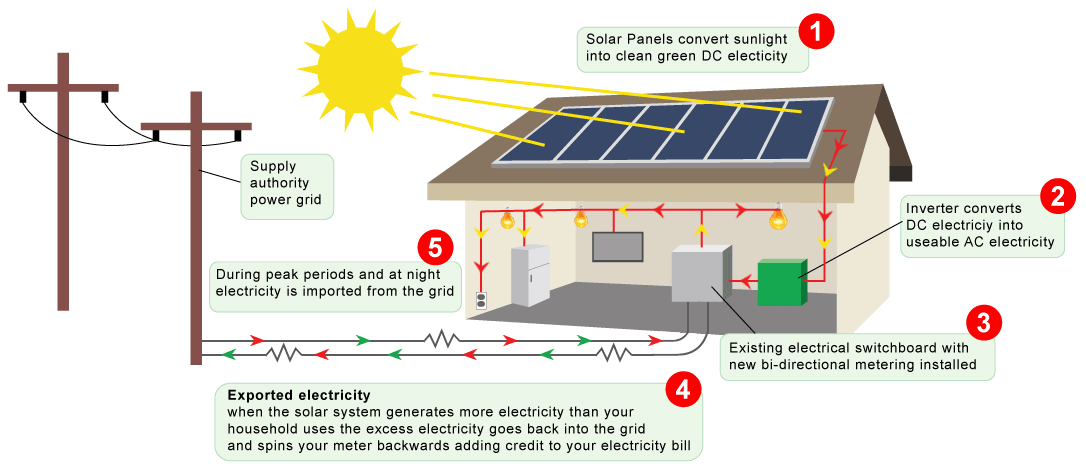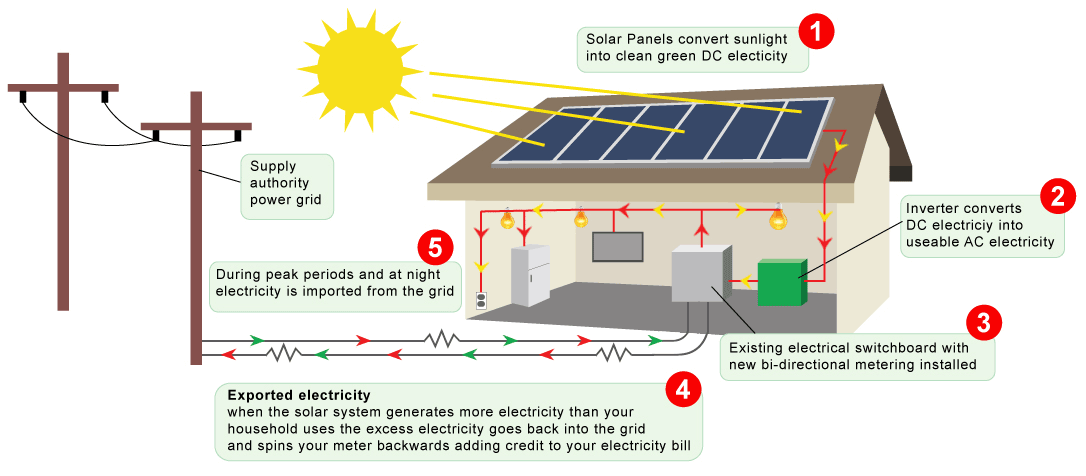
An on-grid solar system is a type of solar power setup that is connected directly to the public electricity grid. It generates electricity using solar panels and supplies it to the grid via a grid-tied inverter. This system does not require batteries, as any excess power generated is sent to the grid and drawn back when needed.
Key Components of an On-Grid System:
-
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
-
Grid-Tied Inverter: Converts DC into alternating current (AC) which is compatible with the electrical grid and household appliances.
-
Net Meter: Measures the energy imported from and exported to the grid, enabling net metering benefits.
-
Grid Connection: Links the solar system to the local utility grid.
How Does It Work?
-
During the day, solar panels absorb sunlight and produce electricity.
-
The inverter converts this electricity to AC for home or business use.
-
If your solar system generates more power than you consume, the excess is sent to the grid.
-
At night or on cloudy days, when solar production is low, you draw electricity from the grid.
This seamless integration ensures a constant and reliable power supply, leveraging both solar energy and the utility grid.
Benefits of On-Grid Solar Systems
✅ Cost-Effective
Since there is no need for battery storage, the initial investment is lower compared to off-grid systems.
✅ Net Metering Advantage
Users can earn credits for the excess electricity they feed into the grid, effectively reducing monthly electricity bills.
✅ Low Maintenance
Fewer components mean reduced maintenance. Inverters may need occasional service, but solar panels typically last 25+ years.
✅ High Efficiency
Direct grid connection allows efficient use of electricity without storage losses.
Limitations of On-Grid Systems
-
⚠️ No Power Backup During Outages: Since the system is dependent on the grid, it shuts down during power failures for safety reasons (unless paired with a hybrid inverter or backup).
-
⚠️ Dependent on Utility Policies: Net metering benefits depend on the local government and utility provider’s regulations.
Ideal Applications
-
Residential homes in urban or semi-urban areas
-
Commercial buildings
-
Factories and warehouses
-
Institutions like schools and hospitals
On-grid systems are especially suitable where grid reliability is good and policies favor solar adoption.
Conclusion
The on-grid solar system is a smart and sustainable solution for reducing electricity bills, lowering carbon footprints, and contributing to a greener planet. As solar technology becomes more affordable and policies become more favorable, the future is bright—literally powered by the sun.
Whether you’re a homeowner or a business, going solar with an on-grid system is a forward-thinking investment in both environmental responsibility and financial savings.