Harnessing the Power of the Sun: A Closer Look at Solar Panels
As the world faces growing concerns over climate change, pollution, and energy security, renewable energy sources have taken center stage. Among them, solar panels have emerged as a leading solution, offering a clean, sustainable, and increasingly affordable way to generate electricity. This article explores how solar panels work, their types, benefits, challenges, and why they play a critical role in shaping our energy future.
What Are Solar Panels?
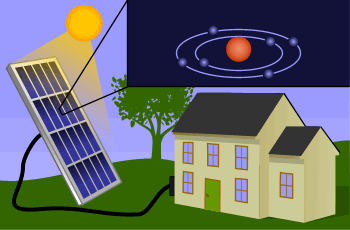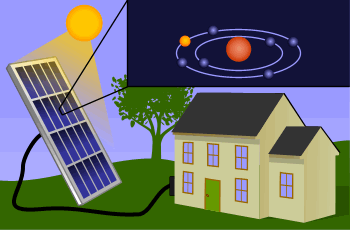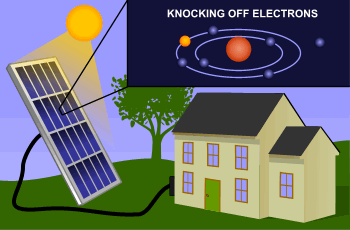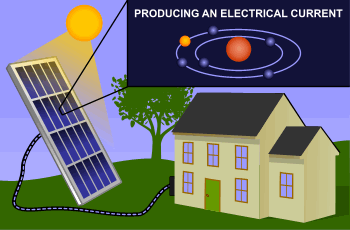
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are typically mounted on rooftops, open fields, or integrated into building materials. Made up of many solar cells, usually composed of silicon, solar panels utilize the photovoltaic effect—a process in which solar energy knocks electrons loose in a material, generating an electric current.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
The basic functioning of a solar panel involves the following steps:
-
Sunlight hits the solar cells, generating energy through the photovoltaic effect.
-
This creates direct current (DC) electricity.
-
An inverter then converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is used in homes and businesses.
-
The electricity is either used immediately, stored in batteries, or fed back into the electrical grid.
Types of Solar Panels
There are three main types of solar panels, each with unique characteristics:
-
Monocrystalline Panels
-
Made from single-crystal silicon.
-
High efficiency (18%–22%).
-
Long lifespan and space-efficient.
-
Higher cost.
-
-
Polycrystalline Panels
-
Made from multiple silicon crystals.
-
Moderate efficiency (15%–17%).
-
More affordable.
-
Slightly larger surface area required.
-
-
Thin-Film Panels
-
Made from materials like cadmium telluride or amorphous silicon.
-
Lightweight and flexible.
-
Lower efficiency (10%–13%).
-
Ideal for special applications, such as curved surfaces.
-
Advantages of Solar Panels
Solar panels offer a host of environmental and economic benefits:
-
Renewable Energy Source: Sunlight is free, abundant, and sustainable.
-
Reduced Electricity Bills: Homeowners and businesses can save significantly on energy costs.
-
Low Maintenance: Most solar systems require minimal upkeep beyond occasional cleaning.
-
Environmentally Friendly: No greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution during operation.
-
Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on fossil fuels and centralized grids.
Challenges of Solar Panel Adoption
Despite their benefits, solar panels come with some challenges:
-
High Initial Cost: Installation and setup can be expensive, though prices are dropping and incentives are available.
-
Weather Dependent: Performance can drop on cloudy or rainy days.
-
Energy Storage Needs: Solar power is intermittent, requiring batteries or hybrid systems for consistent supply.
-
Space Requirements: Large-scale systems need significant space for installation.
Future of Solar Technology
Innovation in the solar industry is moving rapidly. Emerging technologies such as bifacial panels, perovskite cells, solar shingles, and transparent solar glass promise higher efficiency and more versatile applications. Coupled with advances in battery storage and smart grid systems, solar power is expected to play a central role in a global clean energy transition.
Conclusion
Solar panels are more than just a clean energy solution—they represent a path toward a more sustainable, self-sufficient, and economically viable energy future. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to cut utility costs or a business aiming to reduce your carbon footprint, solar technology offers a bright and promising solution. As technology advances and awareness grows, solar panels will continue to power homes, industries, and innovations around the world.